How to Use the Cardiovascular Subpanel
The cardiovascular system involves the heart as well as the blood vessels throughout the body. The heart is one of the most important muscles in the human body, and regular care ensures that the heart keeps pumping blood efficiently and effectively.
- The contents of this user manual will consist of the following:
- Heart Rate
- Heart Sounds/Murmurs
- Precordial Palpation
- JVP/Neck Veins
- ECG
- General Notes
- This user manual will start on the General Examination form, Review of Systems panel.

- To access ENT and Ophthalmology, the user will need to open a General Examination form. For more information regarding the General Examination form, please refer to the user manual: General Examination Overview.
- Click on the Review of Systems panel.
- The Review of Systems panel will expand.
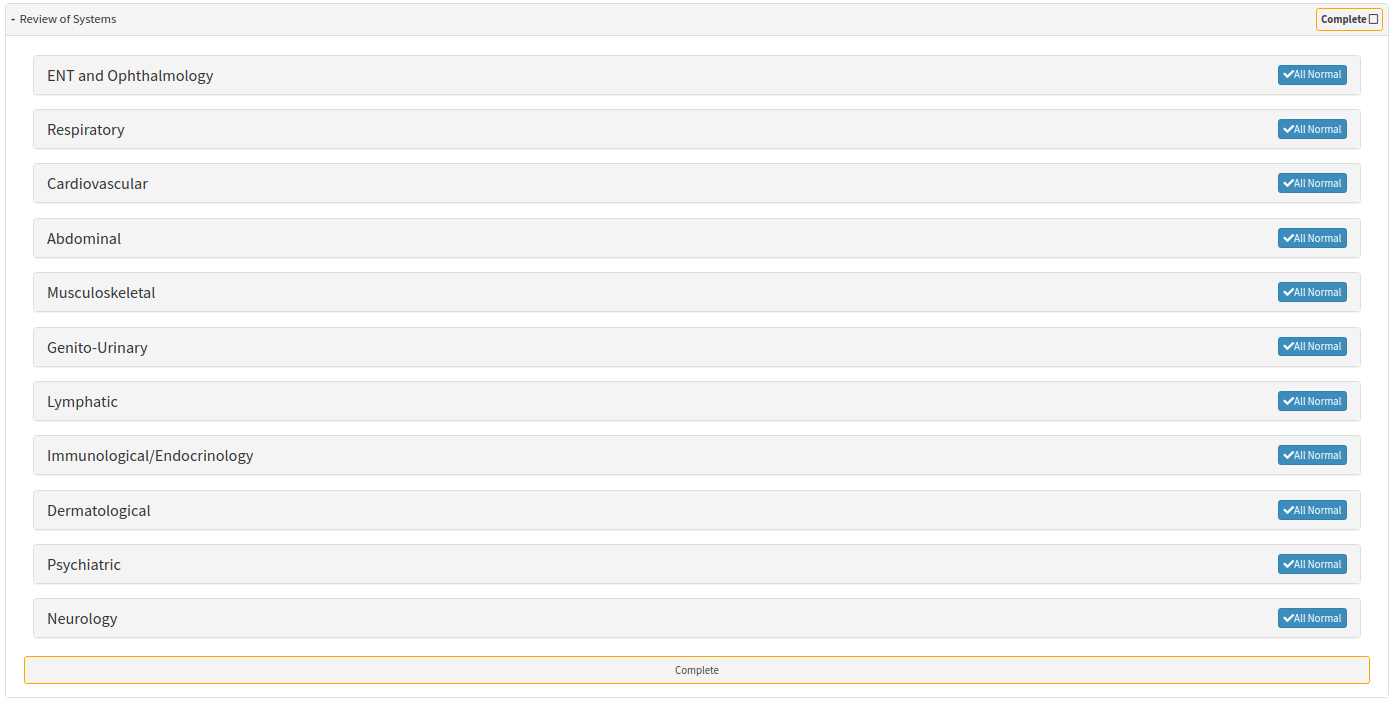
- Click on the Cardiovascular sub-panel.
![]()
- The Cardiovascular sub-panel will expand.
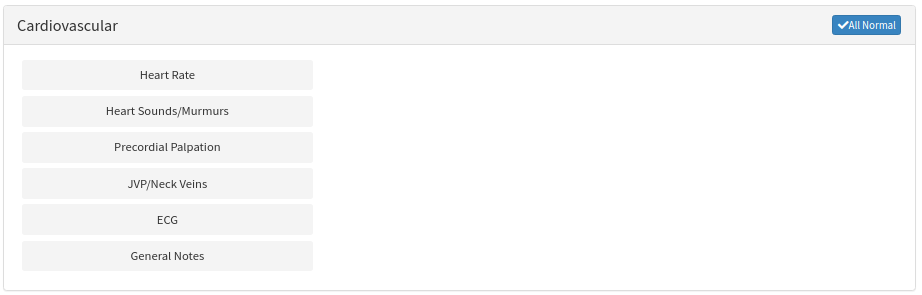
Heart Rate
Heart Rate is the pace at which the heart beats. The speed is measured by the number of beats over a time span of a minute, and the outcome is an important factor in the general health of the Patient.
- Click on the Heart Rate button once to indicate that the Heart Rate has been examined.
![]()
- The Heart Rate button will turn green, which is an indication of normal results.
![]()
- Click on the Heart Rate button a second time, which turns the button red. The red is an indication that results were logged within the button and is not within the normal range.

- Click in the General Notes text box to make any necessary notes. The General Notes field is a free text field.

Heart Sounds/Murmurs
Heart sounds are categorised as the sound generated by the shutting valves inside the heart, once the blood has rushed through a chamber. A murmur is described as an unexpected, additional sound caused by abnormal blood flow through a valve, and is important to diagnose in a Patient.
- Click on the Heart Sounds/Murmurs button once to indicate that the Heart Sounds/Murmurs have been examined.
![]()
- The Heart Sounds/Murmurs button will turn green, which is an indication of normal results.
![]()
- Click on the Heart Sounds/Murmurs button a second time, which turns the button red. The red is an indication that results were logged within the button and is not within the normal range.
- Additional options will also become available
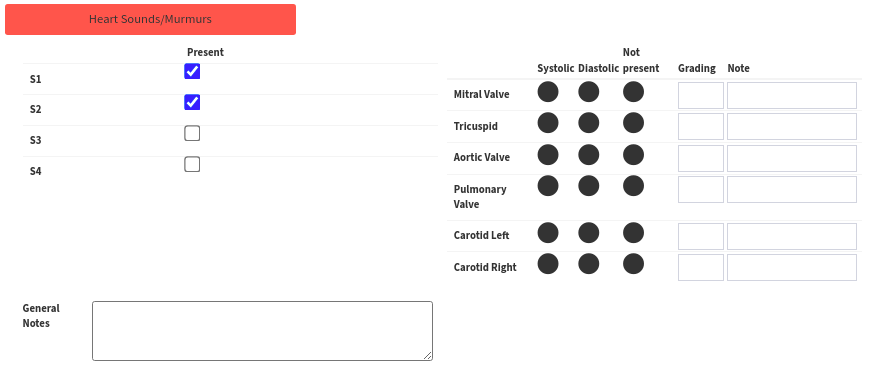
- An explanation for each additional field can be found below.

- S1, S2, S3 & S4: The 4 different sounds produced by the heart are referred to as Sound 1, Sound 2, Sound 3 and Sound 4.
- Sound 1 is made when the contraction of both ventricles occur, sending blood away from the heart.
- Sound 2 is the closing of the valves when the ventricles relax. Vibrations are made when the closing occurs.
- Sound 3 is caused by blood rushing from the atria, into the relaxed ventricles.
- Sound 4 only occurs in abnormal circumstances, and is caused by a stiff ventricle vibrating when the atria forcibly contracts.

- Mitral Valve: The mitral valve is found in the left side of the heart, and ensures that the flow of blood from the left atrium to the left ventricle is kept in the right direction.
- Tricuspid: The tricuspid valve is found in the right side of the heart, and ensures that the flow of blood from the right atrium to the right ventricle is kept in the right direction.
- Aortic Valve: The aortic valve is also referred to as the main outflow valve for the left side of the heart, and is located between the left ventricle and the aorta.
- Pulmonary Valve: The pulmonary valve is found between the right ventricle and the pulmonary artery, and is responsible for the transport of deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs.
- Carotid Left: The left carotid artery is an artery that directly branches off the arch of the aorta. Carotid arteries supply blood to the brain, head and face.
- Carotid Right: The right carotid artery is an artery that branches off of the brachiocephalic trunk of the heart. Carotid arteries supply blood to the brain, head and face.

- These are the different phases of the cardiac cycle that the heart goes through to pump blood.

- Systolic: The part of the cardiac cycle when the heart contracts, and pumps blood out of its chambers into the arteries.

- Diastolic: The part of the cardiac cycle when the heart relaxes, allowing the chambers to fill up with blood.

- Not present: If the Practitioner is unable to determine whether systolic or diastolic pressure is present in the tested area, the user will tick the Not Present checkbox.

- Grading: Grading is done on a scale of 1 - 6. With 1 being very quiet or barely audible, and 6 being very loud.

- Note: The Note field is used to make any additional notes that the Practitioner can refer back to.
- Click in the General Notes text box to make any necessary notes. The General Notes field is a free text field.

Please Note: Click on the Heart Sounds/Murmurs button for a third time to deselect the button, and collapse all of the information found within it.
Precordial Palpation
Precordial Palpation is the examination of the chest wall directly above and around the heart, only using one's hands. The importance of the Practitioner performing a Precordial Palpation is to determine if the heart is of correct size, shape and is positioned in the correct place.
- Click on the Precordial Palpation button once to indicate that Precordial Palpation has been occured.
![]()
- The Precordial Palpation button will turn green, which is an indication of normal results.
![]()
- Click on the Precordial Palpation button a second time, which turns the button red. The red is an indication that results have been logged within the button and is not within the normal range.

- Click in the General Notes text box to make any necessary notes. The General Notes field is a free text field.

Please Note: Click on the Precordial Palpation button for a third time to deselect the button, and collapse all of the information found within it.
JVP/Neck Veins
JVP is also referred to as the jugular venous pressure observed on the right side of the Patient's neck. A high JVP will be indicated with prominent neck veins and can be diagnosed by the Practitioner by measuring those veins.
- Click on the JVP/Neck Veins button once to indicate that the JVP/Neck Veins have been examined.
![]()
- The JVP/Neck Veins button will turn green, which is an indication of normal results.
![]()
- Click on the JVP/Neck Veins button a second time, which turns the button red. The red is an indication that results have been logged within the button and is not within the normal range.

- Click in the General Notes text box to make any necessary notes. The General Notes field is a free text field.

Please Note: Click on the JVP/Neck Veins button for a third time to deselect the button, and collapse all of the information found within it.
ECG
An ECG is also known as an electrocardiogram and is used to quickly and painlessly diagnose any heart defects. An ECG comprises of electrodes, which the Practitioner places on strategic points of the body, that sends electrical signals from the body to a machine that prints the signals out in a readable form.
- Click on the ECG button once to indicate that the ECG has been examined.
![]()
- The ECG button will turn green, which is an indication of normal results.
![]()
- Click on the ECG button a second time, which turns the button red. The red is an indication that results have been logged within the button and is not within the normal range.

- Click on the Add Image button.
- The Video Capture screen will open.
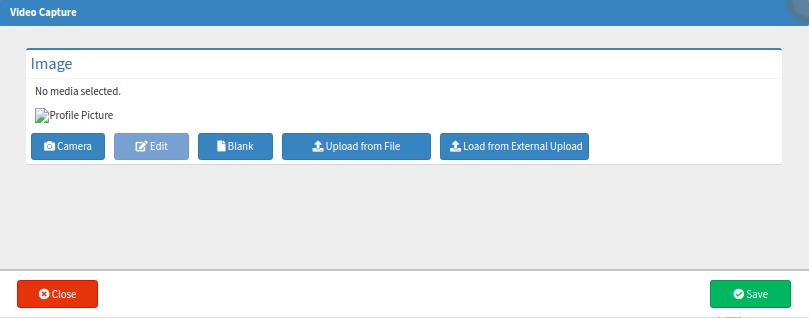
- For more information regarding the Video Capture screen, please refer to the user manual: How to Upload an Image/Photo
- Click on the Close button to return to the Cardiovascular panel.
![]()
- Click in the General Notes text box to make any necessary notes. The General Notes field is a free text field.

Please Note: Click on the ECG button for a third time to deselect the button, and collapse all of the information found within it.
General Notes
Any additional notes can be made within the General Notes button.- Click on the General Notes button once to indicate that notes have been made.
![]()
- The General Notes button will turn green, which is an indication that no changes were made.
![]()
- Click on the General Notes button a second time, which turns the button red. The red is an indication that notes were logged within the button.
- Click in the General Notes text box to make any necessary notes. The General Notes field is a free text field.

Please Note: Click on the General Notes button for a third time to deselect the button, and collapse all of the information found within it.