How to Use the Neurology Subpanel
Neurology is the specialised branch of medicine dealing with the brain and nerves of the human body, and its nervous system. The Practitioner will perform a series of physical examinations to evaluate the nervous system for any possible sensory issues such as Parkinson's, Epilepsy, Cerebal Palsey, and various other neurological disabilities.
- The contents of this user manual will consist of the following:
- Cranial
- Dermatomes
- Reflexes
- Sensory System
- Motor System
- General Notes
- This user manual will start on the General Examination form, Review of Systems panel.

- For more information regarding the General Examination form, please refer to the user manual: General Examination Overview.
- Click on the Review of Systems panel.
![]()
- The Review of Systems panel will expand.
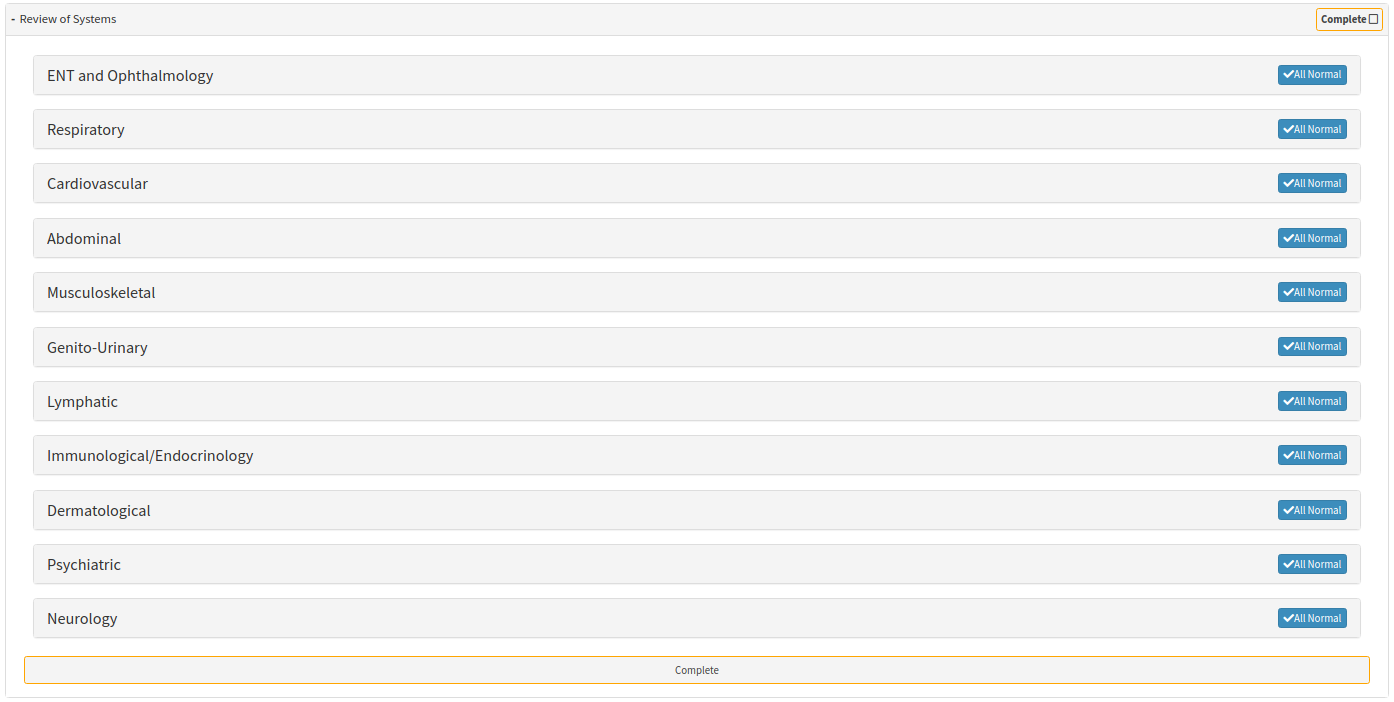
- Click on the Neurology sub-panel.
- The Neurology sub-panel will expand.
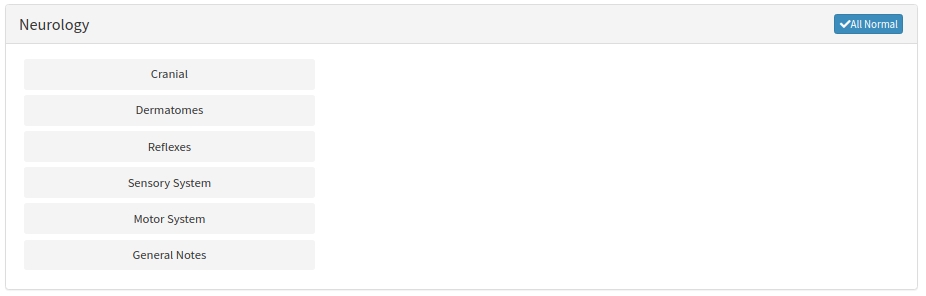
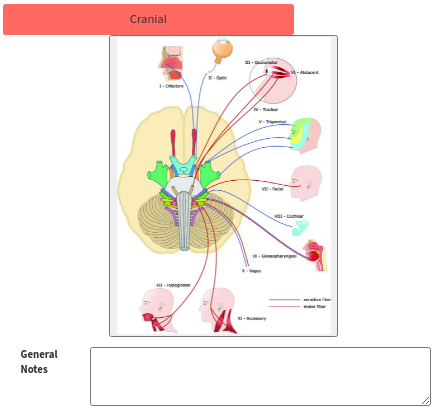
Cranial
A cranial nerve examination is done by testing the various senses and reflexes of the human body. The Practitioner will test the Patient's sense of smell, sight, hearing and sensitivity to touch. Muscles movements and reflexes of the eyes, facial muscles including the tongue, as well as swallowing reflexes are checked over. Any issues regarding sensory or motor function can be discovered during the cranial nerve exam.
- Click on the Cranial button once to indicate that the eyes have been examined.
![]()
- The Cranial button will turn green, which is an indication of normal results.
![]()
- Click on the Cranial button a second time, which turns the button red. The red button indicates that the logged results are not normal.
- Click on the image to open the Video Capture screen.
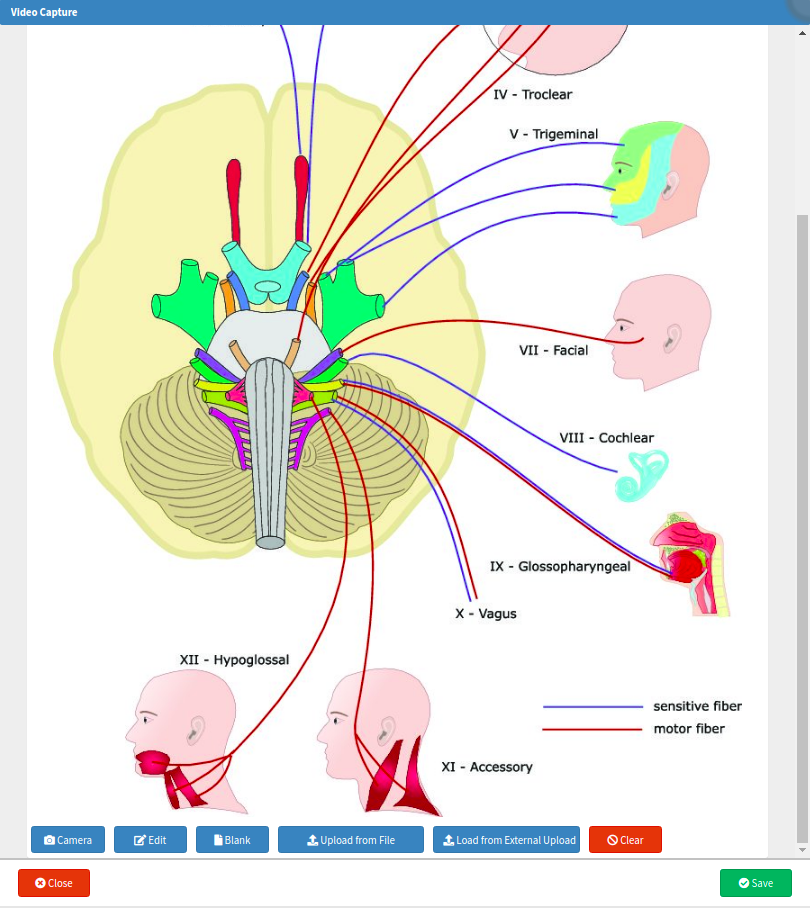
- For more information regarding the Video Capture screen, please refer to the user manual: How to Upload an Image/Photo.
- Click on the Close button to return to the Neurology panel.
![]()
- Click in the General Notes text box to make any necessary notes. The General Notes field is a free text field.

Please Note: Click on the Cranial button for a third time to deselect the button, and collapse all of the information found within it.
Dermatomes
Dermatomes are areas of skin that contain sensory neurons stemming from a singular spinal nerve. Testing dermatomes gives better insight into any nerve damage occurring within the Patient, and is done by subjecting the Patient to various stimuli on certain areas of the skin.
- Click on the Dermatomes button once to indicate that the eyes have been examined.
![]()
- The Dermatomes button will turn green, which is an indication of normal results.
![]()
- Click on the Dermatomes button a second time, which turns the button red. The red button indicates that the logged results are not normal.

- Click on the image to open the Video Capture screen.
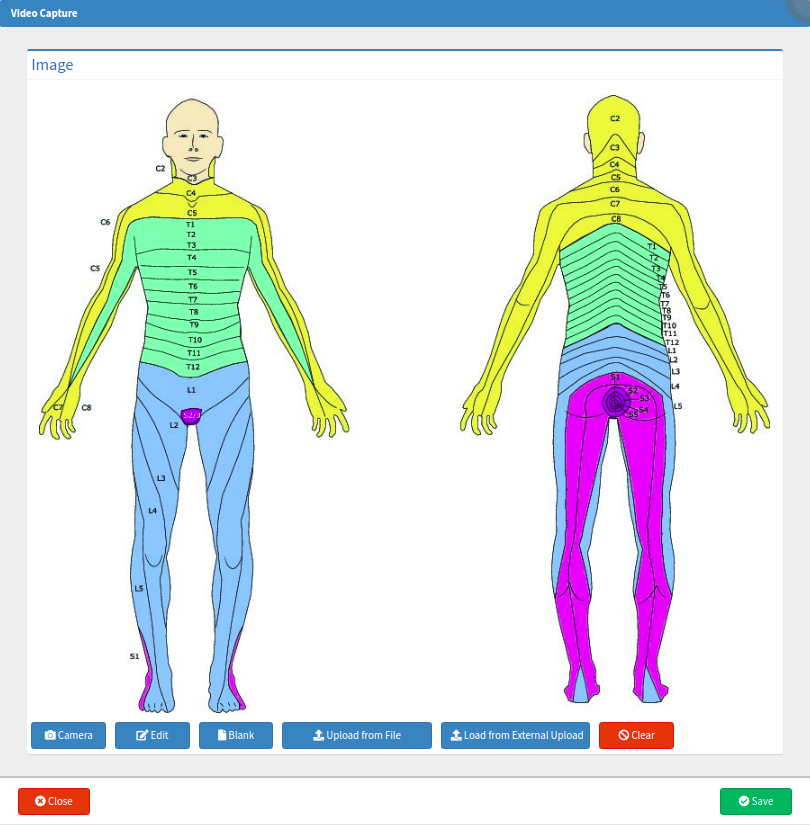
- For more information regarding the Video Capture screen, please refer to the user manual: How to Upload an Image/Photo.
- Click on the Close button to return to the Neurology panel.
![]()
- Click in the General Notes text box to make any necessary notes. The General Notes field is a free text field.

Please Note: Click on the Dermatomes button for a third time to deselect the button, and collapse all of the information found within it.
Reflexes
Reflexes are involuntary, physical responses produced by external stimuli such as a change in light that causes the expansion or restriction of the pupil. The Practitioner can perform various assessments to determine the effectiveness of the Patient's reflexes, and any slow or absent reflexes could mean that nerve damage has occurred.
- Click on the Reflexes button once to indicate that the eyes have been examined.
![]()
- The Reflexes button will turn green, which is an indication of normal results.
![]()
- Click on the Reflexes button a second time, which turns the button red. The red button indicates that the logged results are not normal.
- Additional options will also become available.

- An explanation for each additional field can be found below:
- Abdominal: The Practitioner can stimulate the abdominal muscles with a stroke of a piece of cotton wool, hoping to cause a flex response of the muscles within the abdomen.
- Ankle: The ankle reflex is also known as the Achilles reflex and is triggered when the Achilles tendon is stimulated with a tap of a reflex hammer whilst the foot is in a relaxed, hanging position.
- Brundzinsky: The Brundzinski test is done to detect the possible presence of meningitis or encephalitis, and is done by flexing the Patient's neck upwards from a lying position. If the Hips and knees of the Patient flex, it is seen as a possible indication of underlying issues.
- Elbow: The elbow reflex is more commonly known as the tricep reflex, and is done to ensure that the motor system is functioning as it should.
- Frontal/Glabellar: Found between the eyebrows, above the nose, the glabella is the area of skin and muscles that is responsible for frowning. The glabellar reflexes are tested by repetitively tapping the glabella, and abnormal results could be an indication of underlying neurological issues.
- Knee: The most common reflex is the knee reflex, and is done by tapping the area just below the Patient's kneecap.
- Mentum: The mentum reflex is also known as the palmomental reflex, and is predominantly found in healthy infants. The reflex is activated through the stimulation of the palm of the hand with a light stroke, and causes the flexing of the chin muscles.
- Moro: The moro reflex is more commonly known as the startle reflex, and is present in infancy. The presence of the moro reflex is a sign of a normal central nervous system.

- Testing reflexes on both sides of the body is very important, therefore the fields are broken up into two parts. The first is the left side.

- Testing reflexes on both sides of the body is very important, therefore the fields are broken up into two parts. The second is the right side.
![]()
- Increased: An increased response of a reflex may be an indication of the deterioration of neurons.
![]()
- Absent: The absence of a reflex could be an indication of disruption to either a motor or sensory nerve.
![]()
- Decreased: A decreased reflex response may be an indication of a compressed nerve within the nervous system.
- Click in the General Notes text box to make any necessary notes. The General Notes field is a free text field.

Please Note: Click on the Reflexes button for a third time to deselect the button, and collapse all of the information found within it.
Sensory System
The basic senses such as smell, taste, touch, sight and sound are processed by the sensory system, and alert the body to any external changes to the surrounding environment.
- Click on the Sensory System button once to indicate that the eyes have been examined.
![]()
- The Sensory System button will turn green, which is an indication of normal results.
![]()
- Click on the Sensory System button a second time, which turns the button red. The red button indicates that the logged results are not normal.
- Click on the image to open the Video Capture screen.

- For more information regarding the Video Capture screen, please refer to the user manual: How to Upload an Image/Photo.
- Click on the Close button to return to the Neurology panel.
![]()
- Click on the General Notes text box to make any necessary notes. The General Notes field is a free text field.

Please Note: Click on the Sensory System button for a third time to deselect the button, and collapse all of the information found within it.
Motor System
The part of the nervous system that works with the movement of the body is referred to as the motor system.
- Click on the Motor System button once to indicate that the eyes have been examined.
![]()
- The Motor System button will turn green, which is an indication of normal results.
![]()
- Click on the Motor System button a second time, which turns the button red. The red button indicates that the logged results are not normal.

- Click on the General Notes text box to make any necessary notes. The General Notes field is a free text field.

Please Note: Click on the Motor System button for a third time to deselect the button, and collapse all of the information found within it.
General Notes
Any additional notes can be made within the General Notes panel.- Click on the General Notes button.
![]()
- The General Notes button will turn green, which is an indication that no changes were made.
![]()
- Click on the General Notes button a second time, which turns the button red. The red button indicates that the logged results are not normal.
- Click on the General Notes text box to make any necessary notes. The General Notes field is a free text field.

Please Note: Click on the General Notes button for a third time to deselect the button, and collapse all of the information found within it.
- Click on the Close button to exit the Clinical Case screen without saving.
- Click on the Save and Close drop-up arrow for more options:
- Click on the Save button to save the information captured on the form.
- Click on the Save Lines To New Macro button to save the lines captured as a Macro.
- Click on Save and Close to save the form or the changes made.
![]()