Create a Service Centre
Creating a Service Centre allows the Practitioner to set up various locations where Patients will be treated.
Certain criteria should be taken into consideration when creating a service centre:
- What type of services will be offered at the centre.
- Where will the location of the Service Centre be, such as In Hospital.
- What the level of treatment will be in the specific Service Centre, for example, High Care.
- As what type of facility will the Service Centre be classified as, for example, a Hospital in-patient facility.
A Service Centre is a place where medical care and treatment are provided to Patients. A Service Centre will determine the type of facility where consultations and treatment will occur. Service Centres will indicate whether the Patient was treated at the Hospital or in the Practitioner consulting rooms. The information about where the treatment took place, will also determine the rates that are charged and how the Patient is covered by their Medical Aid. A Service Centre can be a standalone facility or a department within a larger Hospital or healthcare organisation. Service Centres typically offer a range of diagnostic, therapeutic, and preventive healthcare services, including primary care, specialist consultations, lab tests, imaging, and other types of medical procedures. Some Service Centers may also provide preventive care services such as vaccines and screenings, as well as rehabilitation and other types of support services.
Please Note: In a Hospital/Day Clinic setting each ward will have their own Service Centre, which assists with the set-up of Bed Management for example, a Pharmacy will also be a Service Centre as well as a Theatre. For more information regarding Bed and Facility Management, please refer to the chapter: Bed & Facility Management.
- Log in to the GoodX Desktop using your GoodX username and password.
- From the Navigator Double Click on the MedDebs Module.

- The Debtor Manager screen will open.
- Click on Lists on the menubar.
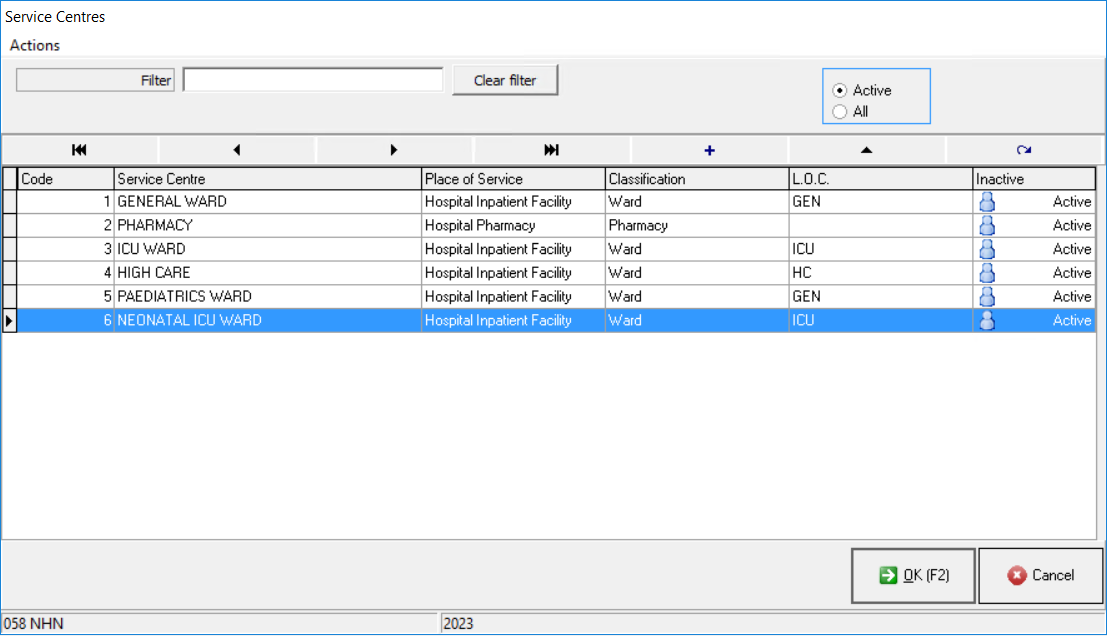
- Click on Service Centres on the submenu.
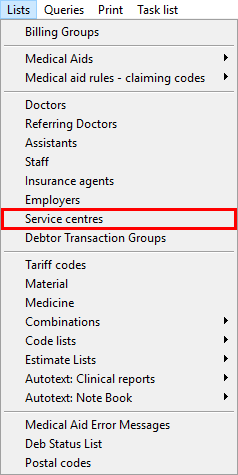
- The Service Centres screen will open.
- Click on the + button in order to create a new Service Centre.
![]()
- The Service Centre screen will open.
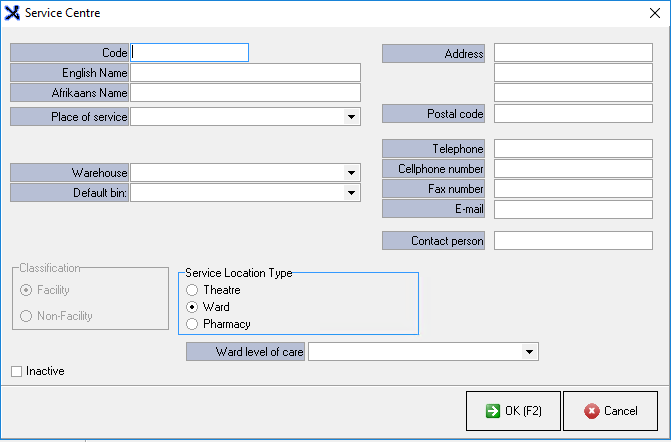
- An explanation will be given for each field and option on the Service Centre screen.
![]()
- Code: A unique alphanumeric number which identifies the Service Centre.
![]()
- English Name: An English name for the Service Centre.
![]()
- Afrikaans Name: An Afrikaans name for the Service Centre.
![]()
- Place of Service: The location where medical care is provided to a Patient. The Place of Service is important for determining the appropriate level of care for a Patient and for determining the payment for the medical services provided.
- Click on the Place of Service drop-down menu to select the appropriate option.
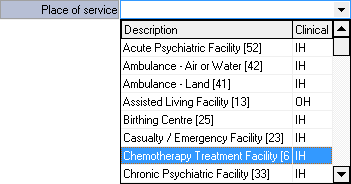
- Select an option from the list which has become available:
- Acute Psychiatric Facility: An In-patient psychiatric facility or psychiatric Hospital, is a type of medical facility who provides intensive, short-term treatment for Patients with severe mental illness or emotional distress. These facilities are designed to provide a safe and structured environment for Patients who need round-the-clock care and supervision while they receive treatment for their mental health condition.
- Ambulance - Air or Water: A water or aircraft used to transport Patients who require emergency medical attention. Water and Air Ambulances are specifically designed and equipped to treat Patients whilst in transit.
- Ambulance Land: Ambulances are vehicles which are specifically designed and equipped to transport Patients who require medical attention to a Hospital or other medical facility. Land Ambulances travel on easily accessible roads and terrains.
- Assisted Living Facility: A residential facility who provides housing, personal care, and health-related services to seniors and other adults who need some assistance with daily living activities, but do not require the round-the-clock medical care provided in a nursing home. Assisted Living Facilities typically offer a range of services, including help with dressing, bathing, and grooming, as well as medication management and supervision.
- Birthing Centre: A facility which is specifically designed and equipped to provide care for women during childbirth. Birthing Centres are typically staffed by midwives, nurse practitioners, and other healthcare professionals who are trained in childbirth and women's health.
- Casualty/Emergency Facility: Also known as an Emergency Department (ED) or Emergency Room (ER), is a facility which is specifically designed and equipped to provide immediate medical care to Patients with acute illnesses or injuries. Casualty/Emergency Facilities are typically located in Hospitals or stand-alone clinics, and are open 24 hours a day, seven days a week.
- Chemotherapy Treatment Facility: A medical facility which specialises in the administration of chemotherapy to cancer Patients. Chemotherapy Treatment Facilities are typically located in Hospitals, cancer centres, or stand-alone clinics, and are staffed by oncologists and other medical professionals who are trained in chemotherapy administration.
- Chronic Psychiatric Facility: Also known as a long-term psychiatric facility or in-patient psychiatric facility, is a type of medical facility which provides intensive, long-term treatment for Patients with severe and persistent mental illness. These facilities are designed to provide a safe and structured environment for Patients who need round-the-clock care and supervision while they receive treatment for their mental health condition.
- Consulting Room: A private, enclosed space in a medical or healthcare facility where a Practitioner, such as a Practitioner or a nurse, can meet with Patients to discuss their medical condition, treatment options, or other healthcare-related matters.
- Day Clinic/Hospital: An outpatient surgery centre which provides surgical procedures and other medical treatments on a same-day basis. Day Clinics/Hospitals are typically less expensive and more convenient than Hospital-based surgery, as Patients are able to receive treatment and go home on the same day, rather than staying overnight in the Hospital.
- Field Hospital: A temporary medical facility which is set up in a disaster or conflict zone to provide emergency medical care to victims of a disaster or conflict. Field Hospitals are typically equipped with a range of medical equipment and supplies, and are staffed by Practitioners, nurses, and other medical professionals who are trained to provide emergency care in challenging environments.
- Frail Care Facility: A nursing home or a long-term care facility, is a type of residential facility which provides housing and comprehensive medical care for seniors or Patients with chronic medical conditions who require ongoing support and supervision. Frail Care Facilities provide round-the-clock care to residents.
- Home: Home care is a type of medical and personal care which is provided to Patients in their own homes. Home care services are designed to help Patients manage their health conditions, recover from illness or injury, and maintain their independence while living at home.
- Homeless Shelter: Homeless Shelters are facilities who provide temporary housing and support services to Patients who are experiencing homelessness. Homeless Shelters can provide basic medical care, such as treatment for minor injuries or illnesses, or referrals to outside medical Practitioners for more specialised care.
- Hospice: A facility which provides medical care to Patients who are facing a terminal illness or who are in the advanced stages of a chronic medical condition. Hospice care is designed to help Patients manage their symptoms and improve their quality of life, rather than to cure their illnesses.
- Hospital In-patient Facility: Provides Hospital-level care to Patients who are admitted to the Hospital for an overnight stay or longer. In-patient Facilities are used to care for Patients who require a high level of medical attention or who are unable to care for themselves at home, including Patients who are recovering from surgery, Patients with chronic medical conditions, or Patients with severe or critical medical conditions.
- Hospital Outpatient Facility: Provides medical care to patients who do not require an overnight stay in the Hospital. Outpatient Facilities are used to care for patients who are able to return home after receiving medical treatment, which include Patients who are recovering from surgery, Patients with chronic medical conditions, or Patients who need follow-up care after being discharged from the Hospital.
- Hospital Pharmacy: Located within a Hospital or healthcare facility. Hospital Pharmacies provide a range of services, including filling prescriptions for medications, providing information about the safe use of medications, and helping Patients to manage their medications. Hospital Pharmacies may also offer over-the-counter (OTC) medications and other healthcare products, such as vitamins and medical equipment.
- Independent Pharmacy: A type of pharmacy which is not affiliated with a Hospital or other healthcare facility. Independent Pharmacies are typically owned and operated by a pharmacist or group of pharmacists and are located in stand-alone stores or in other retail locations.
- In-patient Psychiatric Hospital: Provides Hospital-level care to Patients with mental health conditions or behavioural health issues. In-patient Psychiatric Hospitals are used to care for Patients with severe or complex mental health conditions or behavioural health issues who require a high level of care and support. May include Patients who are experiencing acute symptoms, such as suicidal thoughts or psychosis, or who are unable to manage their mental health condition on an outpatient basis.
- In-patient Rehabilitation Facility: A medical facility which provides comprehensive rehabilitation services to Patients who are recovering from an illness or injury. In-patient Rehabilitation Facilities are used to care for Patients who are recovering from an illness or injury and who require a high level of rehabilitation services. Which may include Patients who have experienced a stroke, a spinal cord injury, or a traumatic brain injury, or who are recovering from surgery or another medical condition.
- In-patient Substance Abuse Rehabilitation Centre: Provides comprehensive treatment and support to Patients who are struggling with substance abuse or addiction and who require a high level of treatment and support. These facilities are typically recommended for Patients who have severe substance abuse problems or who are unable to manage their substance abuse on an outpatient basis.
- Mass Immunisation Centre: A medical facility which is specifically designed to provide large-scale vaccination administration to the general population. Mass Immunisation Centres are typically set up in response to outbreaks of infectious diseases or in preparation for natural disasters or other emergencies.
- Military Treatment Facility: A medical facility which is operated by the Military and provides medical care to military personnel and their families. These facilities are typically located on or near military bases and may be available to military personnel and their families regardless of their location.
- Mobile Unit: A type of medical facility which is designed to be transported to different locations to provide medical care to Patients in remote or underserved areas as well as rural communities, or disaster-affected areas.
- Nursing Facility: Provides long-term or rehabilitative care to Patients who are unable to care for themselves or who require a high level of medical or personal support as well as Patients with chronic medical conditions or provides rehabilitation services to Patients who are recovering from an illness or injury.
- Oncology Facility: Dedicated to the diagnosis, treatment, and management of cancer. Oncology Facilities are used to care for Patients with cancer or who are at risk of developing cancer.
- Other Place of Service: A term used to describe a healthcare setting which does not fit into any of the other designated categories of healthcare facilities.
- Outpatient Psychiatric Facility: Provides mental health services to Patients on an outpatient basis. Outpatient Psychiatric Facilities are used to care for Patients with mental health conditions or behavioural health issues who do not require Hospitalisation or who are able to manage their condition on an outpatient basis. These facilities are typically recommended for Patients with mild to moderate mental health conditions or behavioural health issues.
- Outpatient Rehabilitation Facility: A medical facility which provides rehabilitation services to Patients on an outpatient basis. Outpatient Rehabilitation Facilities are used to care for Patients who are recovering from an illness or injury and who require rehabilitation services but do not require Hospitalisation or who are able to manage their rehabilitation on an outpatient basis. These facilities are typically recommended for Patients with mild to moderate rehabilitation needs.
- Outpatient Substance Abuse Rehabilitation Facility: A type of medical facility who provides treatment and support to Patients who are struggling with substance abuse or addiction on an outpatient basis, who are struggling with substance abuse or addiction and who do not require Hospitalisation or who are able to manage their substance abuse on an outpatient basis.
- Place of Employment/Work Site: The provision of healthcare services to employees at their place of work. Medical care at a place of employment or work site is typically provided as a benefit to employees and is often funded by the employer. Onsite medical care can be convenient for employees, which allows them to access medical care and support services without having to leave their place of work.
- Prison Correctional Facility: The provision of healthcare services to inmates who are incarcerated in a prison or other correctional facility. Medical care at a prison or correctional facility is typically funded by the Government agency responsible for the facility.
- Private Laboratory: Privately owned and operated, which provides laboratory testing and other diagnostic services to Patients and healthcare Practitioners.
- Psychiatric Halfway House Facility: A residential facility which provides supportive housing and other services to Patients with mental health conditions who are transitioning from in-patient psychiatric care to independent living. Typically recommended for Patients who are able to live independently with support and who are at risk of Hospitalisation due to their mental health condition.
- Public Central Hospital (Level 3): Owned and operated by the Government and provides a high level of medical care to the general public. Public Central Hospitals are typically funded by the Government and may provide care to uninsured or underserved populations. These Hospitals are typically equipped to provide a high level of medical care, including specialised procedures and advanced technologies, and are often used as referral centres for other Hospitals in the region.
- Public Day Hospital: Owned and operated by the Government and provides medical care to the general public on a day-patient basis. Patients at a public day Hospital receive medical care during the day but do not stay overnight at the Hospital.
- Public District/Provincial Hospital: Provides medical care to the general public in a specific geographic region. owned and operated by the Government.
- Public Health Pharmacy: Owned and operated by the Government which provides prescription medications and other pharmacy services to the general public at little to no cost. Public Health Pharmacies may not have the same range of medications and pharmacy products as other pharmacies, and Patients may need to obtain medications from other sources.
- Public Infectious Disease Hospital: A medical facility which is owned and operated by the Government and provides specialised medical care to Patients with infectious diseases, including serious or life-threatening conditions. These Hospitals typically serve as a primary source of medical care for Patients with infectious diseases in their geographic region and may also serve as referral centres for other Hospitals in the region.
- Public Laboratory: Provides laboratory testing and other diagnostic services to the general public. Public Laboratories are typically funded by the Government and may provide care to uninsured or underserved populations. Public laboratory services may be limited in scope and may not be comparable to the level of care which is available in private healthcare settings.
- Public Psychiatric Hospital (Level 2): Used to care for Patients with a wide range of mental health conditions, including serious or complex conditions. Public Psychiatric Hospitals are typically funded by the Government and may provide care to uninsured or underserved populations.
- Public Regional Hospital (Level 2): Cares for Patients with a wide range of medical conditions and injuries, including serious or complex conditions. These Hospitals typically serve as a primary source of medical care for the general public in their geographic region and may also serve as referral centres for other Hospitals in the region.
- Public Specialist Healthcare Facility: Cares for Patients with a wide range of medical conditions and injuries, including serious or complex conditions. These facilities may provide care for specific medical conditions, such as cancer, cardiovascular disease, or mental health conditions, or they may provide care for specific Patient populations, such as children or the elderly.
- Public Trauma or Emergency Facility: A type of medical facility which is owned and operated by the Government and provides emergency medical care to the general public. Funded by the Government and may provide care to uninsured or underserved populations.
- Radiology Facility: Provide diagnostic imaging and other radiology services to Patients. The results of these tests are typically used to diagnose medical conditions, monitor the effectiveness of treatment, or assess the overall health of a Patient.
- Radiotherapy Treatment Facility: Used to provide specialised radiation therapy services to Patients with cancer and other conditions which can be treated with radiation. The goal of radiotherapy is to destroy or damage cancer cells or other abnormal cells in the body, while minimising the impact on normal healthy cells.
- Renal Dialysis Facility: A type of medical facility which provides specialised kidney dialysis services to Patients with kidney failure or other conditions which require dialysis. Dialysis is a medical treatment which filters the blood to remove waste and excess fluids when the kidneys are not functioning properly.
- Rural Health Clinic: Provide a convenient and accessible source of medical care to the general public in rural areas and serve as a critical resource for Patients living in these areas.
- School: Medical services are provided to students, faculty, and staff at educational institutions, such as Primary schools, High schools, Colleges, and Universities. Services may include a range of services, such as preventative care, diagnostic testing, treatment, and support services, such as counselling and social services. These services may be provided on-site at the educational institution or may be accessed through referral to other healthcare Practitioners in the community.
- State or Local Public Health Clinic Step-down Facility: Provide specialised medical care and rehabilitation to Patients who have been discharged from the Hospital but still require additional care. These facilities may serve as a transition between the Hospital and the Patient's home and may provide care for a range of medical conditions, including serious or complex conditions.
- Telehealth: The use of electronic communication and information technologies, such as phone, video, and internet, to provide healthcare services and support to Patients remotely. Telehealth can be used to connect Patients with healthcare Practitioners and other medical professionals. A convenient and accessible option for Patients, particularly those who live in rural or underserved areas, or who have mobility issues or other challenges which make accessing in-person healthcare difficult.
- Temporary Lodging: Interim housing arrangements which are provided to Patients or their caregivers during medical treatment or recovery. Provided by Hospitals, healthcare facilities, or other organisations and may be located on or near the medical facility where the Patient is receiving treatment.
- Traditional Medicine Outlet: Provide Alternative medical treatments, such as herbal remedies, acupuncture, and other types of natural, and traditional treatments.
Please Note: Each Service Centre has a Clinical description to advise what type of Service Centre each option is:
- OH: The Service Centre is an out-of-hospital facility. The Patient is not required to stay over and the facility is not equipped for Patients to stay the night.
- IH: The Service Centre is an In Hospital facility. Patients can be admitted for treatment and stay overnight for short and long periods.
![]()
- Warehouse: The place where stock for the specific Service Centre is kept.
- Click on the Warehouse drop-down menu to select the desired Warehouse from the list that has become available.
Please Note: The Warehouses that will appear, are the Warehouses which have already been set up. For more information regarding how to create a Warehouse, please refer to the user manual: Setup of the Warehouses.
![]()
- Default Bin: The place where items are placed within a Warehouse, by default, such as a cupboard, a trolly or a shelf. The Default Bin will always be the general bin where movement takes place, which is always directly linked to the Warehouse.
- Click on the Default Bin drop-down menu to select the desired Bin from the list that has become available.
Please Note: The Default Bins that will appear, are the Bins which have already been set up. For more information regarding how to link a Bin to a Warehouse, please refer to the user manuals: Bin Linking.

- Address: The permanent physical address where the Service Centre is located.
![]()
- Postal Code: A postal code associated with the physical address of the Service centre.
![]()
- Telephone Number: A landline number where the Service Centre can be contacted.
![]()
- Cellphone Number: The cellular or mobile number of the Service Centre which can be used as an alternative number, if the landline number can be reached or in case of an emergency.
![]()
- Fax Number: A number which the Service Centre can send and receive facsimile documents from.
![]()
- Email: A electronic mailing address where the Service Centre can be contacted.
![]()
- Contact Person: The name of the main person which can be contacted at the Service Centre.
- Classification: An Indication to advise whether a Service Centre is a Facility or Non-Facility.
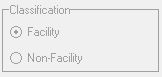
- Facility: A registered medical facility where a Patient can receive treatment, such as a Hospital, Clinic or Day Clinic.
- Non-Facility: Treatment will take place which is not typically set up as a treatment facility, where there is a Practitioner, Nurse or Emergency responder who is able to assist, such as a School, Home, or Outpatient Facilities.
Please Note: Once the Place of Service is selected, the Classification will be selected automatically.
- Service Location Type: What the Service Centre is classified as.
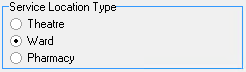
- Theatre: An Operating Room (OR) which is sterile and well-equipped, where surgeons perform surgical procedures on Patients. A Theatre is located inside a Hospital or surgery centre.
- Ward: A section of a Hospital which is dedicated to the care of patients with a specific type of illness or injury. Wards consist of many rooms in which Patients' care is monitored by medical staff.
- Pharmacy: A healthcare facility which is licensed to dispense medications to Patients. Pharmacies are typically located in Hospitals, Supermarkets, or stand-alone stores, and are staffed by Pharmacists.
![]()
- Ward Level of Care: The level of care provided in a Hospital ward is determined by the severity of the Patient's condition and the intensity of the treatment required.
- Click on the Ward Level of Care drop-down menu to select the relevant option from the list which has become available.
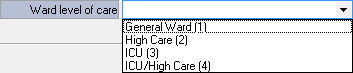
- Select an option from the list which has become available:
- General Ward: Provides medical care to Patients with a variety of medical conditions or for Patients who are recovering from surgery or other medical procedures.
- High Care: Patients who have a high level of dependency and require a greater level of support and assistance with activities of daily living.
- ICU: Intensive Care Unit - Hospital units or departments which provide specialised medical care to critical Patients with serious or complex medical conditions, such as severe injuries, illnesses, or disabilities.
- ICU/High Care: Care is provided to a combination of critical Patients and Patients who are not as critical, but still need close monitoring.
![]()
- Inactive: The Service Centre is no longer in use. When a Service is marked as inactive the user will longer be able to select or use the specific Service Centre until marked as active.
- Tick the Inactive check box to mark the Service Centre as inactive.
- Tick the Inactive check box to mark the Service Centre as inactive.
- Click on the Cancel button to close the Service Centre screen without saving.
![]()
- Click on the Ok (F2) button to save the changes of the new Service Centre which has been created. The Service Centre screen will close and return to the Service Centres screen.
- The new Service Centre which has been created will now appear on the Service Centres screen.
- Click on the Cancel button to close the Service Centre screen and return to the Debtor Manager screen.
![]()
- Click on the Ok (F2) button to save the changes and close the Service Centre screen and return to the Debtor Manager screen.