Best Practice Guidelines: Healthcare Practice Management & POPIA Compliance Framework
Best Practice Guidelines: Healthcare Practice Management
&
POPIA Compliance Framework
Copyright © 2021 GoodX Software. All rights reserved.
GoodX online Learning Centre
learning.goodx.co.za
9. Billing: Roles & Purpose
9.2. Tariffs & Terminology
Medical Aids tend to update their tariffs during price season (January every year) and to tweak prices throughout the year. It is therefore important to keep your GoodX up to date with the newly released tariffs by importing the new tariffs via the internet into your GoodX Software's PostgreSQL database.
GoodX Standard Rates: (What GoodX provides)
- Standard set of tariff codes.
- Standard set of pricelists per Medical Aid
- Standard prices per code per pricelist
- Standard Medical Aid Contract
- Standard general pricelist Medical Aid linking
- Standard Medical Aid Contract, Pricelist Medical Aid linking
- Standard Billing Groups
Practice Custom / Specific / Private Rates: (What Clients provide)
- Which standard Medical Aids Contracts need to be linked to the Practice Billing Profile
- Any custom codes not supplied as part of the standard code set
- Custom pricelist not part of standard pricelist set
- Custom values/prices to be applied to standard or custom billing codes
- Custom Medical Aid Contracts
- Custom general pricelist Medical Aid linking
- Custom Medical Aid Contract linking
- Custom Billing groups for specific percentages or balanced billing
- Custom Levies per code or pricelist
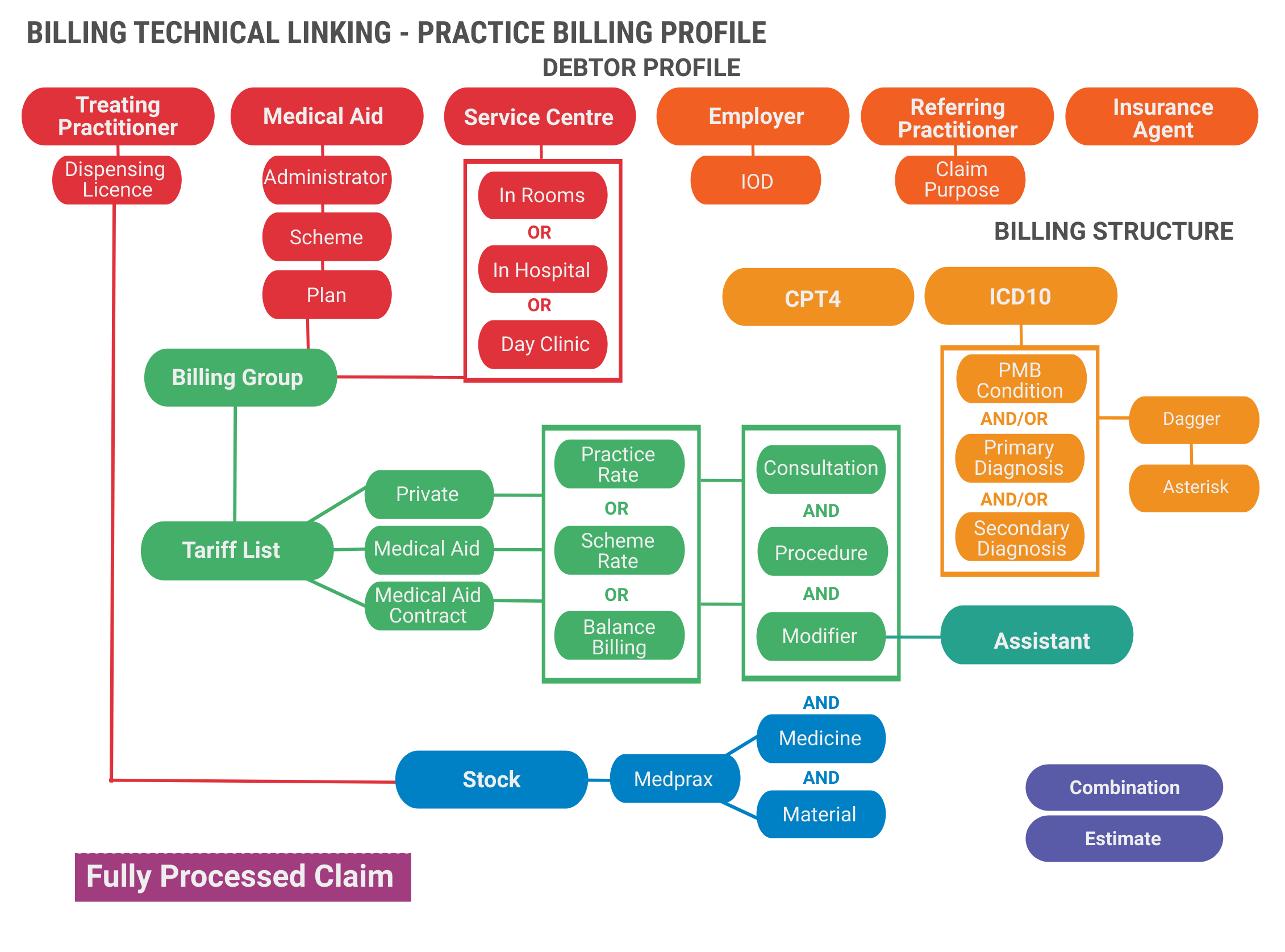
Billing Structure Linking - Practice Billing Profile
TERMINOLOGY
General Terminology in the Practice
Beneficiary
The benefits are paid for by the medical scheme to either the provider (practice) or to the patient.
Consultations/Visit
A consultation/visit refers to a clinical situation where a medical practitioner personally obtains a patient’s medical history, performs an appropriate clinical examination and, if indicated, administers treatment, prescribes or assists with advice. These services must be face-to-face with the patient and exclude the time spent doing special investigations which receive additional remuneration.
Subsequent visits
Refers to a voluntarily scheduled visit performed within four (4) months after the first visit. It may imply taking down medical history and/or a clinical examination and/or prescribing or administering of treatment and/or counselling.
Hospital visits
Where a procedure or operation was done, hospital visits are regarded as part of the normal after-care and no fees may be levied (unless otherwise indicated). Where no procedure or operation was carried out, fees may be charged for hospital visits according to the appropriate hospital or inpatient follow-up visit code.
Normal hours and after hours
After-hours services are paid at the same rate as benefits for normal hours services. Emergency medical services rendered to a patient, at any time, may attract a fee as specified in modifier 0011 and items 0146 or 0147.
Timely
In
the case of cancellation of appointments, "timely" shall
mean 24 hours prior to the appointment.
Patient consent
Mutual decision-making between the doctor and the patient. This is the broadest definition of informed consent. It involves an open exchange of information, education on options and alternatives for care, and assisting the patient in making a decision that is consistent with his/her values. Obtaining the patient’s consent for medical procedures or participation in research trials. This sense of informed consent focuses purely on legal requirements for disclosure rather than shared decision-making.
Practice Terms and Conditions
The terms and conditions pertaining to payment.
Practice Payment Contract
The contract pertaining to payment.
Consumer Protection Act
The Consumer Protection Act, No. 68 of 2008 was
signed on 24 April 2009. To promote a fair, accessible and
sustainable marketplace for consumer products and services.
National Health Act
The National Health Act, 61 of 2003, provides a framework for a single health system for South Africa. The Act provides for a number of basic health care rights, including the right to emergency treatment and the right to participate in decisions regarding one's health. The implementation of the Act was initiated in 2006, and some provinces are engaged in aligning their provincial legislation with the national Act.
National Credit Act
The National Credit Act, 2005. Incidental credit agreements are those agreements entered into between a credit provider (your doctor, vet, etc.) and you to pay within a certain loopholes time (usually within thirty days), or in terms whereof a lower price is payable if you pay by a certain date and the higher price is payable if you pay after that date.
Practice Management Application
The software application the practice is
using to store patient information and keep financial records.
Cash Practice
Time-of-service collections—minimize patient billing
and the risk of not being paid by collecting the patient’s
financial responsibility (including deductibles, coinsurance and
co-payments) at the time of service.
Payment Arrangements
Where the practitioner enters into a payment arrangement with a specific medical scheme/administrator to provide health care services to its members in terms of a payment arrangement.
Billing Terminology
NHRPL 2006
The National Health Reference Price List 2006, as published by the Council for Medical Schemes. The court ruling made in July 2010 declared the publication of the NHRPL invalid and null and void. The whole Healthcare Industry has been forced to fall back to the last CMS (Council for Medical Schemes) published NHRPL of 2006.
Base Price
The base price used for calculating ALL tariff structures is NHRPL 2006.
Pricelist Discipline
A pricelist discipline is a master collection of tariff codes that are used to generate pricelists. Examples of disciplines:
- Medical practitioners codes
- Physiotherapist codes
Price Collection
A price collection is a collection of tariff codes that can be billed in the system. A price collection is subdivided into various pricelists. Individual pricelists are tailored to carry the prices necessary for effective billing in the medical environment. Individual price lists are linked to medical aids in the system. The system then knows which tariffs to charge, based on the medical aid to which the patient belongs. Price collections are linked to a financial year.
DHR
Discovery Health Rate.
MSR
Medical Scheme Rate.
RCF (Rand Conversion Factor)
Rand conversion factor for units as published in the NHRPL 2006 and amended by the SAMA. All codes are divided into different categories what we call GoodX the unit. Each category is given an RCF (Rand Conversion Factor). A unit is allocated a monetary value. A different monetary value is allocated to each unit, based on whether it is a clinical procedure unit, consultative unit, anaesthetic unit, etc.
The monetary value for a service is calculated by multiplying the RVU with the RCF. So in this example above the RVU value is 14 and the RCF is 13,1912.
14 X 13.1912 = 184.70
PMB-rate (Practice Rule)
Regulation 8 of the Medical Schemes Act (131 of 1998 as amended) determines that a medical scheme must pay in full, without co-payment or the use of deductibles for the diagnosis, treatment and care costs of the prescribed minimum benefit condition. This is the practice interpretation of a fair rate for PMB’s (normally a % increase of the MSR or Practice Rate).
Practice Rate
The tariff structure the practice defines as the practice rate – normally this rate is an escalated calculation from NHRPL 2006 or a payment arrangement the practice have in place that they want to benchmark against. This is also considered the “minimum” rate.
Scheme Rate Practice (Traditionally the “Contracted in” Practice)
Practices collect payment in full from the patient medical scheme’s benefits, billing the health insurer.
Out-of-Hospital Tariff
The fee structure the practice uses for billing patients
In-Rooms.
In-Hospital Tariff
The fee structure the practice uses for billing patients In-Hospital.
Standard Rates
The Standard Medical Aid tariffs as provided by the Medical Aids.Custom Rates
Any procedure code or pricing that is not standard from the Medical Aid Price Tariffs.- For example, 0190A instead of 0190 or a 20c difference in price.
- Percentages add on tariff: (Billing Group)
- For example, The Doctor can decide if he/she wants to add 10% etc to the Medical Aid tariff. This gets set up with a Billing Group according to the Doctor's specifications. Any shortfall/difference not paid by the Medical Aid can be set up to be Patient or Medical Aid liable.
Modifiers
Modifiers provide additional information about the service or procedure performed. They are used as an extension to alter a procedure code but not change the code or its definition. Modifiers create various reimbursement consequences for the associated visit, test or procedure.
COID Pricelist
The tariff amounts published in the tariff guide to medical services rendered in terms of the Compensation for occupational injuries and diseases Act.
Insurance Pricelist
The tariff amounts for insurance medical claims as published annually by SANLAM.
Insured Benefits (Also known as “Max Tariffs)
Where the medical aid option makes provision for a maximum cover, more than the scheme rate. Normally this gets specified for in-hospital and out-hospital benefits.
CPT4 Pricelist
Surgicom surgeons contracted to Medihelp may only bill in CPT and are not allowed to combine the SAMA Doctors’ Billing Manual (DBM) or other coding systems. The rand conversion factor (RCF) is negotiated annually with Medihelp. The contract specifically prohibits “balance billing” charges in excess of the agreed amounts and no claims may be made directly from the client, even in the event of disagreement.
Balanced Billing (Co-Payment)
The process of billing a patient for the difference between the medical service provider's actual charges and the amount that the provider will be reimbursed from the patient's medical scheme option. This can also be a fixed co-payment to all patients on consultations, except where a payment arrangement excludes it.
Linking
Each Medical Aid gets linked to their specific Pricelist.- For example, Discovery gets linked to Discovery Rates and Bestmed to Bestmed Rates etc.
Custom Linking Profile
The Practice / Doctor can decide what prices to link with which Medical Aid.- For example, All Medical Aids get linked to Discovery Rates and any shortfall will be Patient Liable.
Billing Groups
A Billing group will tell the system which calculates the price that should use when calculating the tariff price. The billing code will apply certain rules on the tariff code for each medical aid and plan. Each Medical Aid Plan can be linked to a certain Billing Group. Indication at what percentage the Patient will be billed.
- For example, 100% Scheme Rate or 200% above the Medical Aid Scheme Rate
Medical Aids: Administrator
Every medical aid has an administrator who administrator their claims and administration. Some medical aids administer their own medical aid schemes and plans and some medical aids have other Administrators who administer their medical aids for example Bankmed is administered by Discovery health
Medical Aids: Medical Aid Lists
List of all the Medical Aids Options grouped by the Scheme.
Medical Aids: Schemes
Each medical aid has its own schemes which patients can choose from, this is also referred to as a plan.
Medical Aids: Clearance house
Medical aid clearing houses is a third party that handles the claims, billing and switching on behalf of the medical aid doing it themselves.
Medical Aids: Managed care
Managed Care Medical aid list is the list of certain medical aids that are responsible for the medical aids contact information. Each medical aid will be linked to a Managed Care Medical Aid that will manage all this information on their behalf.
Medical Aids: Medical aid EDI switch
Full list of all the Medical Aids and Medical Aid Plans with the Option Codes and the Routing Codes, to indicate which Medical Aids can be switched to Medical Aids.
Medical Aid Contracts (Special Rates Agreements)
These are rates that are negotiated between Clients and Medical Aids.The Client signs a Network Agreement with specific Rates that the Doctor can charge above the standard Medical Aid rates. Specific rules from Medical Aids apply.
Take Note: Registration with a medical aid is not the same as signing a special rates agreement with that medical aid.
Invoice levy
Is defined as a portion of an invoice that the medical aid is not expected to pay. In some cases, the practice will expect the patient to pay this amount directly before leaving the practice after his/her appointment.
Value of the invoice levy price
Is determined by a combination of amounts that the practice predefines and amounts that the medical aid predefines.
Medical aid portion of the levy
A medical aid levy is a percentage or an amount applied to specific medical aid schemes to apply a certain mark-up to billing codes based on the medical aid plan.
Is defined as a portion of a debtor invoice that the medical aid expects the patient to pay. For example, a patient may be expected to pay R10.00 for every medicine item on the invoice. The Medical Aid levy calculation rules are imported from Medprax and displayed on the levy screen. The rules can be edited locally.
Practice portion of the levy
Is defined as a portion of a debtor invoice that the patient is expected to pay as defined by the practice. For example, the patient might be expected to pay a balanced billing portion of R200.00 for a first consultation. The practice portion can also sometimes be auto-generated by the system using billing group rules, or manually captured in GoodX Web.
Medprax
Medprax is a data interface containing medical aids, medicines, and materials information. Medprax is updated once a week if a practice is registered with Medprax.
Medprax updates the following information for medical aids:
- plans
- discontinued plans
- rules
- routing codes
- administrator information and changes
Medprax updates the following information for medicines and materials:
- Nappi codes
- the list price per item
- descriptions (name, strength, size, volume, and presentation)
- discontinued items
- new items
- updated items
GAP cover
An additional cover to a patient medical scheme option that pays for the shortfall between the practice rate and the MSR. Should the practice rate be more, Gap Cover will cover the difference in cost, up to 400%.
Stock PricesMedprax provides SEP (Single Exit Price) rules per medical aid for medicines and materials. Clients can decide to add their own mark-up per medicine or material on the list price provided by Medprax.
Material Stock List
The Material list will show all the material/consumables on Medprax or IQest list and all Medicine the practice did create them selfs. The list will be divided into active and inactive items. When no stock control is used all items will be active. When the Practice has a contract with Medprax or IQest the list will be kept up to date on a weekly or daily basis.
Medicine Stock List
The Medicine list will show all the medication on Medprax or IQest list and all Medicine the practice did create themselves. The list will be divided into active and inactive items. When no stock control is used all items will be active. When the Practice has a contract with Medprax or IQest the list will be kept up to date on a weekly or daily basis.
Medicine Formulary
A medicine formulary is a list of brand-name and generic prescription medication that is approved to be prescribed by a particular health insurance policy, or in a specific health system or hospital. Medicine formularies are developed based on the efficacy, safety and cost thereof.
- These medicines are reimbursed by medical aids for specific chronic conditions.
- They are usually connected to a certain pricing structure to support access to cost-effective medicines.
ICD-10 Codes
ICD-10: International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision. ICD-10 codes are used to indicate the diagnosis of the patient's illness or problem. In basic terms, what is wrong with the patient?
In health care, coding systems are used to differentiate diagnoses and procedures in virtually all treatment settings. Diagnostic and procedural codes are connected to nearly every system and business process in health plans and provider organizations, including reimbursement and claim processes.