An introduction to the protection of personal information in the healthcare practice
3. The meaning of POPIA words
Topics
- Person
- Private body
- Personal Information
- Special Personal Information
- Process
- Record
- Unique identifiers
- Consent
Person
A natural person OR a juristic person. This is a significant difference from the application of the European GDPR, as the GDPR does not include protection of PI of juristic / legal persons.
Private body
A private body means one of three things:
- It can mean a natural person who carries on or has carried on any trade, business or profession, but only in such capacity, in other words a sole proprietor.
- It can mean a partnership which carries or has carried on any trade, business or profession.
- It can mean any former or existing juristic person, but excludes a public body.
Take note: A person can therefore be part of a private body, and a private body is defined in connection to the business or profession and needs to appoint an Information Officer with the Information Regulator.
Personal Information (PI)
Information relating to a person who is
- identifiable;
- living natural / existing juristic.
There is no limited list in the Act, but the following information is included (* is SPI):
- Body - race*, gender, sex life*, pregnancy, sexual orientation, age, colour
- Status - marital, nationality, ethnicity*, social origin
- Medical - health* (physical & mental), well-being, disability, biometrics*
- Beliefs - religion*, conscience, opinions, views, preferences, philosophical beliefs*
- Behaviour - criminal if only alleged / sub iudice*
- Background - language, culture, birth
- Numbers - ID, symbols, email & physical address, tel nr, location, online ID
- Correspondence - original / further identifying to original
- Name if it links person to other personal information
Notes:
- Deceased persons fall outside the ambit of the POPIA.
- This is not a closed list - just examples of PI.
- Biometric is defined as a technique of personal identification that is based on physical, physiological or behavioural characterisation including blood typing, fingerprinting, DNA analysis, retinal scanning and voice recognition - could also include photographs of the person.
Special Personal Information (SPI)
SPI is information pertaining to:
- the religious or philosophical beliefs, race or ethnic origin, trade union membership, political persuasion, health or sex life or biometric information of a DS; or
- the criminal behaviour of a DS to the extent that such information relates to:
- the alleged commission by a DS of any offence; or
- any proceedings in respect of any offence allegedly committed by a DS or the disposal of such proceedings.
May only process with consent of DS, or
- To exercise right / obligation in law / international law
- For statistical & research purposes to serve public interest & disproportionate effort to ask for consent
- Health & sex life: healthcare practitioners / healthcare institutions / insurance co / medical schemes & administrators may process to comply with contract (Sec 32)
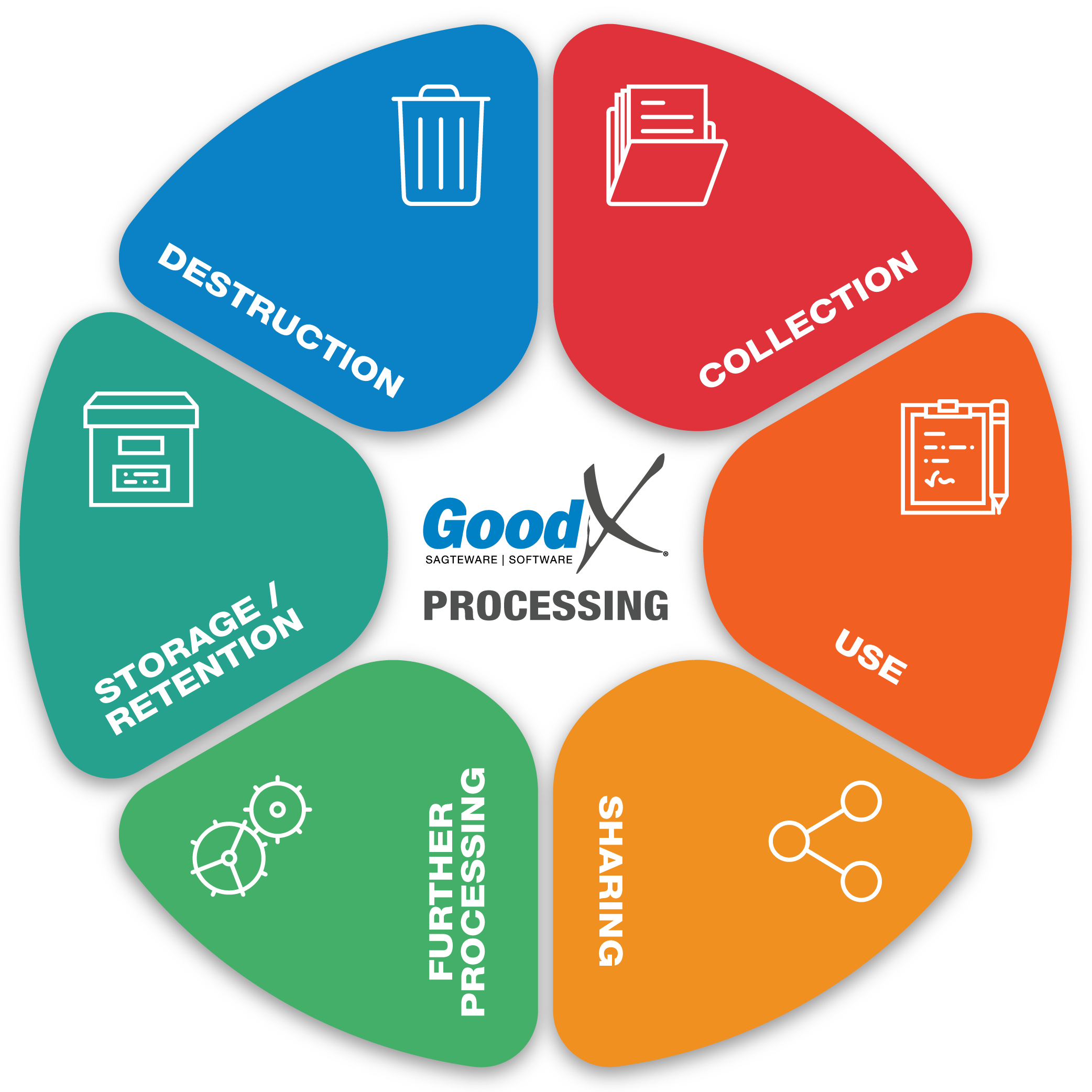 Process
Process
Processing means any operation or activity or any set of operations, whether or not by automatic means, concerning PI, including:
- the collection, receipt, recording, organisation, collation, storage, updating or modification, retrieval, alteration, consultation or use;
- dissemination by means of transmission, distribution or making available in any other form; or
- merging, linking, as well as restriction, degradation, erasure or destruction of information.
Processing of PI must always be done lawfully.
Record
A record is ANY recorded information regardless of form or medium. A record must be in possession OR under control of the RP.
The record does not have to be created by RP and it does not matter when the data came into existence.
Unique identifiers
A unique identifier means any identifier that is assigned to a DS and is used by a RP for the purposes of the operations of that RP and that uniquely identifies that DS in relation to that RP.
The RP may process a unique identifier without the prior authorisation of the IR if:
- the purpose of the processing of the unique identifier is the same for which the identifier was specifically intended at collection and the unique identifier is linked together with information processed by other RPs (e.g. switching to medical aids - the purpose of collection is to submit to the medical aids and link it to the medical aid's database); or
- the RP transfers special personal information or the PI of children to a third party in a foreign country that provides an adequate level of protection for the processing of personal information.
Consent
Consent is
- any voluntary
- specific
- informed expression of will
in terms of which permission is given for the processing of PI.
All three elements of consent MUST be present before there can be lawful consent.