Best Practice Guidelines: Accounting Management
1. Introduction to Accounting Management
1.4. Assets and Liabilities
Assets and Liabilities
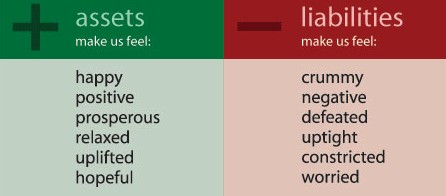
Assets add value to your company and increase your company’s equity, while liabilities decrease your company’s value and equity. The more your assets outweigh your liabilities, the stronger the financial health of your business. But if you find yourself with more liabilities than assets, you may be on the cusp of going out of business.
Assets :
There are 2 types of Assets:
- Current Assets - cash, a cash equivalent, or which can be converted into cash within one year
- Non-Current Assets - A noncurrent asset is an asset that is not expected to be consumed within one year
There are three key properties of an asset:
- Ownership: Assets represent ownership that can be eventually turned into cash and cash equivalents.
- Economic Value: Assets have economic value and can be exchanged or sold.
- Resource: Assets are resources that can be used to generate future economic benefit
Assets are generally classified in three ways:
- Convertibility: Classifying assets based on how easy it is to convert them into cash.
- Physical Existence: Classifying assets based on their physical existence.
- Usage: Classifying assets based on their business operation usage.
- Cash
- Cash Equivalents
- Short-term Investments
- Stock / Inventory
- Marketable securities
- Supplies
Examples of Non-Current Assets or Fixed Assets
- Land
- Buildings
- Equipment / Machinery
- Vehicles
- Furniture and Fixtures
- Accumulated Depreciation (a contra-asset account)
- Intangible fixed assets as Patents
- Trademarks
- Long-term Investments
- Goodwill
- Allowance for Doubtful Accounts (a contra-asset account)
Liabilities :
There are two types of Liabilities
- Current Liabilities (Short-Term Liabilities) is due in one year
- Non-Current Liabilities (Long-Term Liabilities) is due in more than one year
Examples of key ratios that use current liabilities are:
- The current ratio: Current assets divided by current liabilities
- The quick ratio: Current assets minus inventory divided by current liabilities
- The cash ratio: Cash and cash equivalents divided by current liabilities
- Short-term Loans Payable
- Current Portion of Long-term Debt
- Accounts Payable
- Accrued Expenses
- Unearned or Deferred Revenues
- Instalment Loans Payable
- Warranty Liability
- Income Taxes Payable
- Lawsuits Payable
- Bank accounts overdrafts
Examples of Long-Term Liabilities :
- Mortgage Loans Payable
- Bonds Payable
- Long-term notes payable
- Capital Lease
- Deferred tax liabilities
