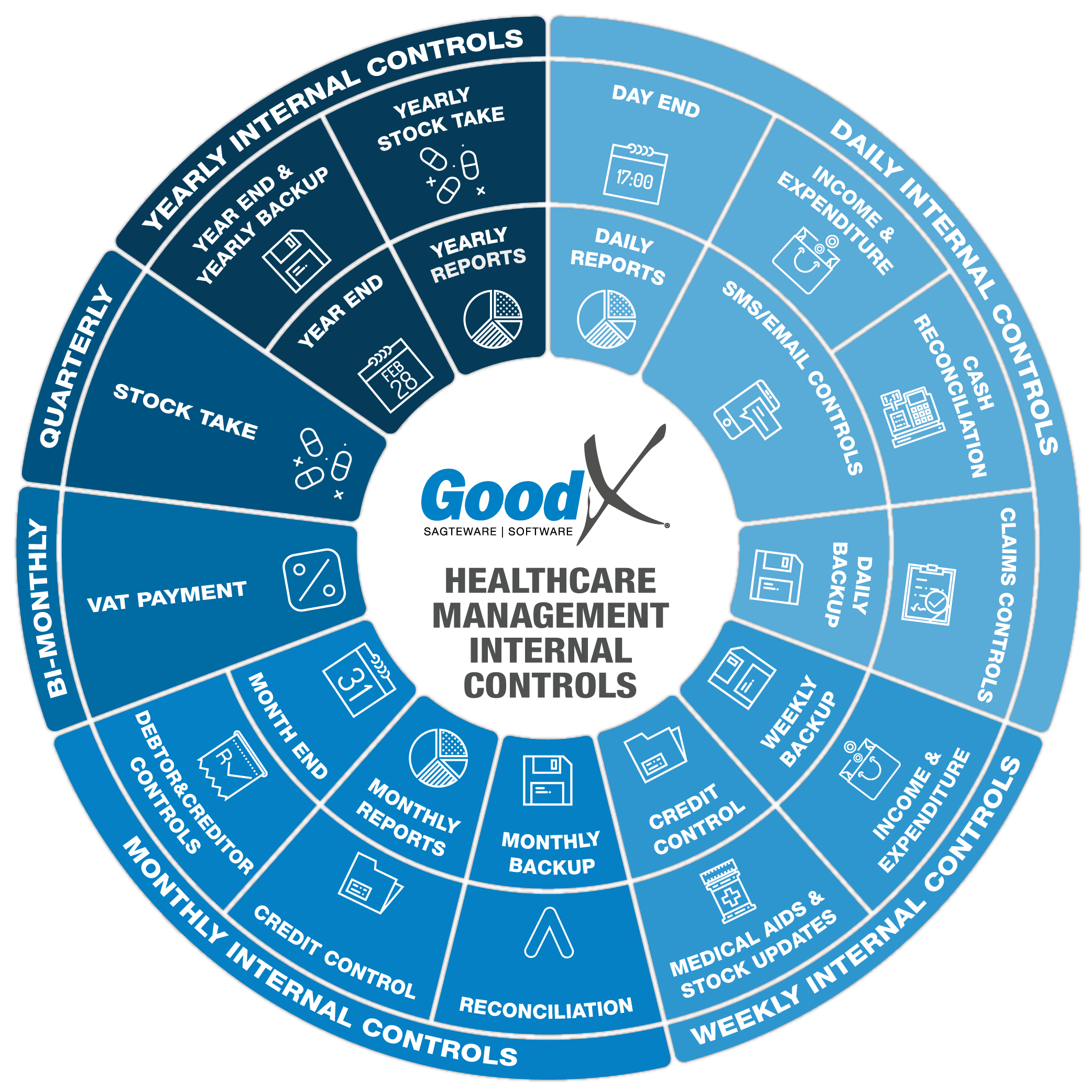
Best Practice Guidelines: Healthcare Management Internal Controls
Best Practice Guidelines: Healthcare Management Internal Controls
Copyright © 2020 GoodX Software. All rights reserved.
GoodX online Learning Centre
learning.goodx.co.za
4. Monthly Internal Controls Summary
4.2. Credit Control

It is important to note that the following persons are ultimately responsible for outstanding medical accounts, despite them contracting a medical aid to pay on their behalf:
- Adult patients (from 18 years and up): they are responsible for their own accounts.
- Minor patients (under 18 years old): their guardians are jointly and severally responsible for their outstanding accounts.
- Main members who sign an agreement with the practice in which they accept full responsibility for payment of any outstanding amounts.
The main member is often seen as the debtor that is responsible for payment of the medical account, but if a patient is an adult, they are responsible for their outstanding accounts even though the main member is indicated as the debtor, unless of course, the main member signed an agreement taking responsibility for the account.
The following steps should be completed monthly:
- Handovers of bad debts to debt collectors or attorneys
- Draw Journal Reports
- Draw the invoices outstanding report
- Draw the unlinked receipt report
- Do batch statement runs
- Draw Age Analysis reports
At this stage, all short payments should have been moved from Medical aid outstanding to Private Patient outstanding. The only Medical Aid outstanding accounts should be:
- Claims are still awaiting responses after being switched; and
- claims awaiting payment from the medical aids after being confirmed.
1. Handovers
Outstanding accounts can be handed over to a debt collecting agency or attorney firm of your choice, who will add their fees to the debtor's account. (Make sure that you have a written agreement with them that all fees and expenses will be collected from the debtor.)
To hand over an account for legal action, the following needs to be in place:
- Notes, which serve as proof that all necessary credit control actions have been performed.
- The detailed account - audit statement.
- The practice should create a bad debt handover form to be completed by the credit controller with the following information:
- Name and Surname of the debtor.
- ID Number of the debtor
- Patient account number
- Amount to be handed over
- The reason why the account should be handed over.
- The form must be approved by management.
- When the account is handed over for collection, a journal should be done to write off the amount to the bad debts account. It will then be removed from the age analysis report and the debtors account will show as zero.
- When the debt is recovered successfully, the written-off invoice amount that has been collected can be moved back to the debtor account with a similar journal and thereafter the payment can be allocated to the invoice.
2. Bad debts written off
Bad debts are overdue accounts that cannot be successfully collected. The outstanding accounts can be written off with journals to the Bad Debts Expense Ledger account.
Take note that only a percentage of bad debts can be written off for tax purposes per financial year. Enquire from your tax consultants or auditors what the percentage is.
3. Journal Report
Only selected users should be allowed to create journals as the function can be abused to commit fraud. Journals are used to:
- Small Balance Write-Off
- Settlement Discount
- Bad Debt Write Off
- Bad Debt Recovered
- Hand Over
- Interest
There should be valid reasons for every journal that is created so that the auditors can evaluate the journals. Keep a Journal report every month to indicate which journals were done and the reasons for each, who the user was and also the date of the transactions.
4. Unlinked Receipt Report
Receipts will be posted as unlinked amounts on accounts when the invoices have not been done yet. As soon as the invoice is done the receipt needs to be linked to the invoice. This will prevent the transactions to be listed on the age analysis with a plus (invoice) and a minus (the unlinked receipt). The Invoice outstanding report will also not balance when the receipts are not linked to the invoices. An unlinked receipt can be corrected with the Autolink function or by doing a Zero receipt.
This needs to be checked on a daily or weekly basis.
5. Invoices outstanding report
Invoices outstanding are all invoices that have not yet been paid by the medical aid or by the patient. The outstanding invoices need to be followed up on and will be part of the credit control process.
A report can be drawn for all the outstanding invoices and you can make sure that this is part of the credit control process. This needs to be checked on a daily or weekly basis.
6. Batch Statement Run
There are two types of statements that can be created:
- The normal statement that only shows outstanding invoices; and
- Audits statements that reflect all transactions on the debtors' account.
The practice will typically send normal statements to patients, but if a patient needs a statement to send to their medical aid or if the patient queries about their statement, an audit statement can be created.
A statement run will send emails of all the outstanding accounts together with a .PDF statement attached to the emails. All accounts that do not have an email account associated with them, will be shown after sending the statement run. Statements can then be printed and mailed to patients. However, the practice can set up their system to automatically print statements that have not been sent by email.
7. Age Analysis Report
The Age Analysis report displays all outstanding accounts and accounts that are in credit, depending on the parameters of the report. Zero balance accounts will also be displayed on the full age analysis and can be filtered out.
The Medical Aid outstanding and the Private Patient outstanding amounts can be marked to show in separate columns.
Make sure that all transactions are up to date before sending the Age Analysis report together with the notes that were created during the month to management for review.
8. Credit Accounts
The credit amounts should be included in the Age Analysis that is sent to management. Credit amounts mean that the outstanding total is less than the actual displayed and can give a wrong impression of the financial status of the practice.
Credit amounts on the Age Analysis should be investigated to understand why there are credits on those accounts. Credits are not the practice's money and should therefore be eliminated as soon as possible.
Credits can be the result of:
- Receipts that were allocated to wrong debtor accounts - these should be corrected so that receipts are posted to the correct debtor accounts and linked properly to their corresponding invoices.
- Receipts that are not linked to their invoices - receipts should be linked to their corresponding invoices to clear the account.
- Payments made by patients and their medical aids, being a double payment on the account - should be refunded to the patient.
- Wrong payments made by medical aids - the credit must be kept until the medical aid reverses the amount on the following remittance.

1. Credit Control on Creditors
Check the following as part of the credit control:
- That all payments were allocated
- Unlinked payments
- Unlinked credit notes
- All debit notes
2. Age Analysis Report
The Age Analysis report displays all outstanding accounts and accounts that are in a debit, depending on the parameters of the report. Zero balance accounts will also be displayed on the full age analysis and can be filtered out.
Ensure that all transactions and debtor notes are up to date for the particular month before sending the Age Analysis report to management for review.