Best Practice Guidelines: Accounting Management
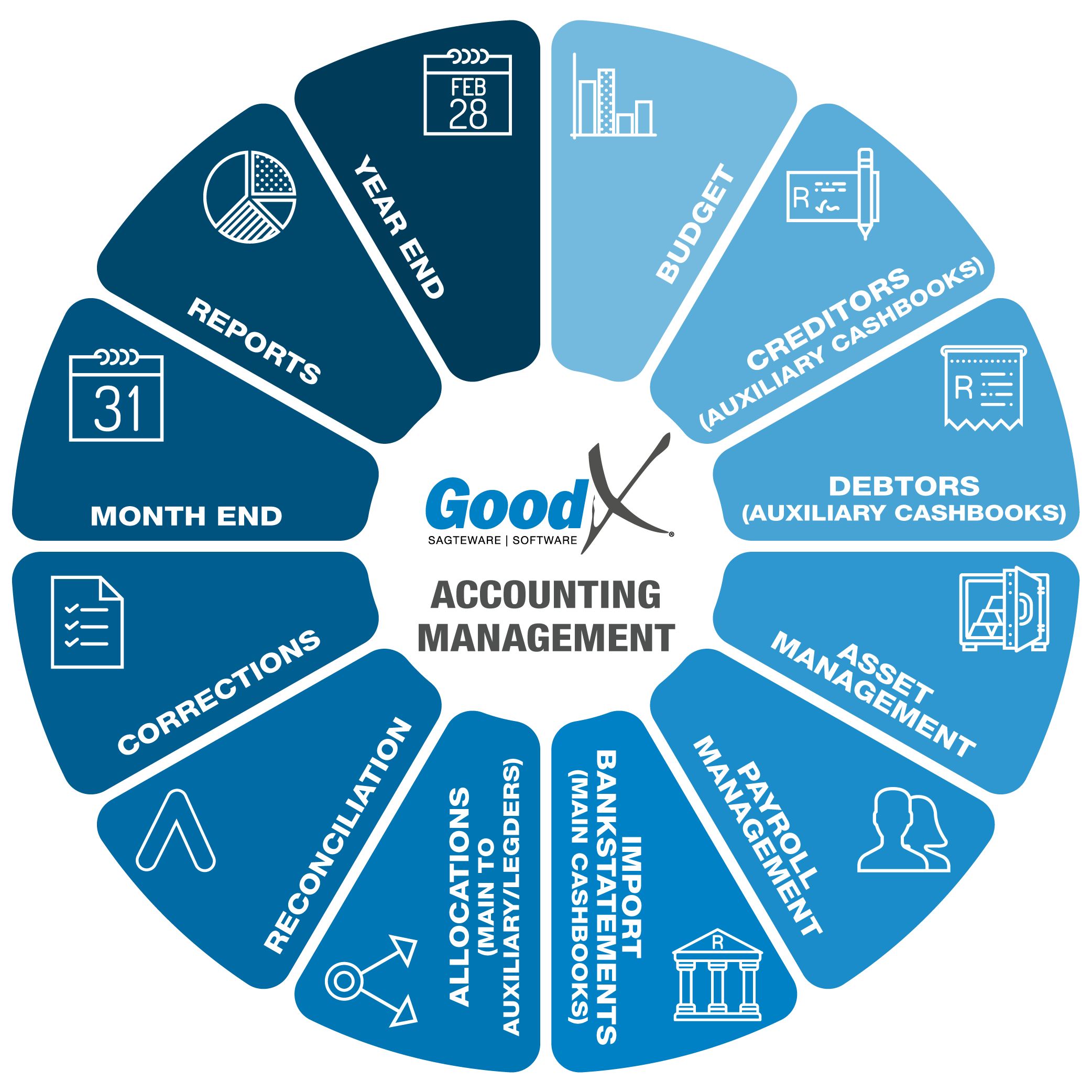
1. Introduction to Accounting Management
1.2. What is Accounting and why does your business need it
The purpose of accounting is to report on all financial transactions within a financial period and reflects the cash flow of practice. This information is used to make decisions about how to manage your practice.
Accounting is divide into different Ledger account:
- Sales ledger (Records accounts receivable)
- Purchase Ledger (Records money spent on purchasing)
- General Ledgers (5 Main Ledger account types)
Accounting is divide into different group levels of General Ledger accounts, the main account types are:
- Assets
- Liabilities
- Income
- Expenses
- Capital / Equity
A General Ledger account is an account or record used to sort and store balance sheet and income statement transactions.
Each main account general ledger has subsidiary ledger accounts or sub-ledgers. A subsidiary ledger or sub-ledger is a ledger designed for the storage of specific types of accounting transactions or contains all the detailed sub-set of transactions. All the transactions that were posted in a subsidiary ledger account will be summarised and display in a Main general ledger account. The total of the transactions in the sub-ledger rolls up into the general ledger.
There are 2 main reports to indicate the summarise of the General ledger accounts and sub-ledger accounts
- Income statement
- Trial balance
Accounting equation :
Assets = Equity + Liabilities
What the business has or own are Assets. How they are financed will indicate if this is a Liability or Capital / Equity.
- By the owner = Capital / Equity
- By other persons (Individuals, Suppliers, Banks etc) = Liabilities