Best Practice Guidelines: Healthcare Management Internal Controls
Best Practice Guidelines: Healthcare Management Internal Controls
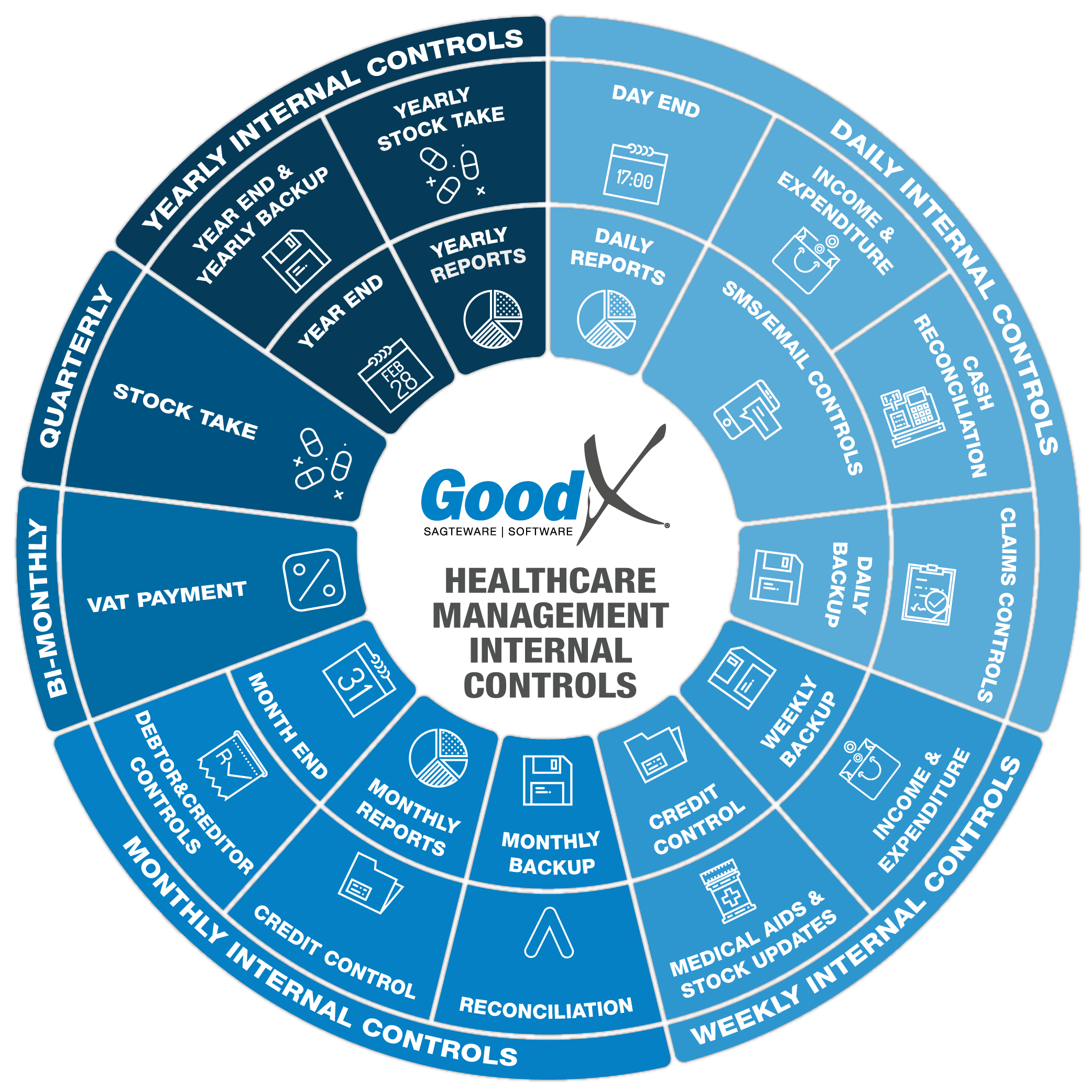
Copyright © 2020 GoodX Software. All rights reserved.
GoodX online Learning Centre
learning.goodx.co.za
1. Introduction to Internal Controls in a Healthcare practice
1.1. Introducing Roles and Responsibilities in the Practice
To run a successful practice a healthcare practitioner must be concerned with all operations of the business and not just the medical aspects of the practice. As the practice grows, practitioners often become unable to perform the routine duties which once gave them control over their business. This lack of control can place the entire practice in jeopardy. Appointing competent personnel will assist the practitioner to ensure that all duties are performed and that the practice is thus run effectively and accurately.
Roles in the practice
 We suggest that the following roles be defined
in the practice. Please note that you do not need to recruit each of these roles, but one person can cover more than one of these roles, depending on the size of your practice. When recruiting staff, you can use these role descriptions to make
sure that the person has all the necessary skills to make your practice a success.
We suggest that the following roles be defined
in the practice. Please note that you do not need to recruit each of these roles, but one person can cover more than one of these roles, depending on the size of your practice. When recruiting staff, you can use these role descriptions to make
sure that the person has all the necessary skills to make your practice a success.
1. Practitioner
Depending on the size of the practice, it is necessary to appoint more practitioners in the practice. The basic functions that a practitioner must be able to perform, are the following:
- Patient consultations
- Physical examinations
- Diagnosis and treatment of illnesses/ailments
- Minor surgery
- Health education
- Practice management and administration
- Liaising with other healthcare professionals and/or hospitals.
2. Practice Manager
The basic functions that a practice manager must be able to perform, are the following:
- To plan, coordinate, direct, and supervise various elements of a medical facility
- Oversee billing and collections, create patient services, and implement employee work policies.
- Daily interactions with employees and patients
- Handle scheduling, technical issues, and daily patient flow
- Analyse and interpret reports and provide feedback to the practice owner(s)
- Implement strategies to make sure the practice's finances are healthy and the practice is profitable.
3. Receptionist
The basic functions that a receptionist must be able to perform, are the following:
- Welcoming patients and visitors by greeting patients and visitors, in person or on the telephone.
- Answering or referring inquiries.
- Optimising patients' satisfaction, the practitioner's time, and treatment room utilisation by scheduling appointments in person or by telephone.
- Keep patient appointments on schedule by notifying the practitioner of the patient's arrival.
- Comfort patients by anticipating patients' anxieties, answering patients' questions, and maintaining the reception area.
- Ensure availability of treatment information by filing and retrieving patient records.
- Maintain patient accounts by obtaining, recording, and updating personal and financial information.
- Check stock to determine inventory level, anticipating needed supplies, place and expedite orders for supplies, verify receipt of supplies, and schedule equipment service and repairs.
- Help patients in distress by responding to emergencies.
- Protect patients' rights by maintaining the confidentiality of personal and financial information.
- Maintain operations by following policies and procedures; reporting needed changes.
- Contributes to team effort by accomplishing related results as needed.
4. Billing Expert
The basic functions that a billing expert must be able to perform, are the following:
- Create invoices based on proper knowledge of medical coding for each consultation and procedure.
- Check the claim history screen to make sure all rejections of claims are dealt with timely and effectively.
- Process billing corrections.
- Submit invoices to medical aids/administrators by electronic data interchange (EDI).
- Submit private patient invoices and statements to clients.
- Follow up on claims submitted to the medical aids/administrators.
5. Cashier
The basic functions that a cashier must be able to perform, are the following:
- Accurately and efficiently operate cash registers.
- Ensure that there is sufficient cash in the cash drawer & enough paper for the card machine.
- Maintain correct cash balances at cash registers.
- Sort, count, and wrap coins and currency.
- Process payments made with cash, checks, credit cards, and debit cards.
- Reconcile cash and card payments at day end.
- Provide outstanding balances on accounts.
- Document payment arrangements.
6. Credit Controller
The basic functions that a credit controller must be able to perform, are the following:
- Maintain strong relationships with all clients to ensure invoices are clear for payment.
- Issue monthly statements to clients.
- Manage the timely and effective collection of all debts and payments.
- Negotiate repayment plans when necessary.
- Resolve all issues raised internally and externally around outstanding invoices.
- Post and allocate daily receipts to accounting systems.
- Post and allocate electronic remittance advice's (ERAs) as received from the medical aids/administrators.
- Run reports for senior staff.
- Provide accounts information to internal departments.
7. Stock Controller
The basic functions that a stock controller must be able to perform, are the following:
- Predict supply and demand to prevent overstocking and running out-of-stock.
- Enter purchase details (suppliers information, invoices and pricing) into GoodX.
- Place orders to replenish stock as needed.
- Track shipments and address any delays.
- Oversee the storage of products, particularly fragile items.
- Evaluate suppliers’ offers and negotiate profitable deals.
- Coordinate regular stock takes and audits.
- Liaise with warehouse staff and other internal teams to test product quality (status upon delivery and storage conditions)
- Keep inventory records updated (including daily shipments)
- Ensure purchases do not exceed the budget.
8. Bookkeeper
The basic functions that a bookkeeper must be able to perform, are the following:
- Purchase supplies and equipment as authorised by management.
- Monitor office supply levels and re-order as necessary.
- Tag and monitor fixed assets.
- Pay supplier invoices in a timeous manner.
- Take all reasonable discounts on supplier invoices.
- Pay any debt as it becomes due for payment.
- Monitor debt levels and compliance with debt agreements.
- Draw the VAT report bi-monthly and remit them to the government.
- Ensure that receivables are collected promptly.
- Record cash receipts and make bank deposits.
- Conduct a monthly reconciliation of every bank account.
- Conduct periodic reconciliations of all accounts to ensure their accuracy.
- Maintain the petty cash fund.
- Issue financial statements.
- Provide information to the external accountant who creates the company’s financial statements, if GoodX's accounting module is not utilised.
- Assemble information for external auditors for the annual audit.
- Calculate and issue financial analysis of the financial statements.
- Maintain an orderly accounting filing system.
- Maintain the chart of accounts.
- Maintain the annual budget.
- Calculate variances from the budget and report significant issues to management.
- Comply with government reporting requirements on SDL, UIF and PAYE.
- Process payroll in a timeous manner.
- Provide clerical and administrative support to management as requested.
- Follow accounting policies and procedures.
Some points to consider
- Appoint competent personnel that can properly fulfil the necessary roles in the practice.
- If you find that a person you are trying to recruit has most of the skills but not all, you can upskill them by sending them for practice management training.
- It is essential that a billing expert must be skilled in medical billing or must take medical billing courses as presented by the different healthcare associations and universities.
- Make sure that all employees know what their roles are in the practice, and what is expected of each role by documenting the roles. A lack of proper role division and work definition can result in required tasks not being completed.
- Ensure a proper separation of duties to prevent fraud in the practice, e.g. choose carefully who may create write-off journals etc.
- Make sure that there is proper software access control in place so that personnel cannot perform unauthorised transactions or actions (e.g. generate reports).
- Establish a monthly meeting to discuss difficulties, solutions to past problems, and operational or employee issues, and allow employees to make constructive recommendations about the operational scope of their functions.
- If controls are not established with the direct involvement of the employees, they will become passive resistors, instead of enthusiastic supporters. Make sure therefore that your employees understand the importance of the controls, and assist them to implement them.
- Provide proper training to staff.